Forklift license additional training (level 2)
Do you want your employees to operate special industrial trucks, such as sideloaders, reach trucks or high-bay stackers? Since the change in the law in 2023, they also need the additional qualification (level 2) in addition to a valid forklift license.
In addition to the theoretical basics, our experienced training instructors teach the necessary skills for safe driving of the industrial trucks in compliance with the DGUV. Participants can then demonstrate their skills directly in the final driving test. Upon successful completion, all graduates receive a certificate of participation.
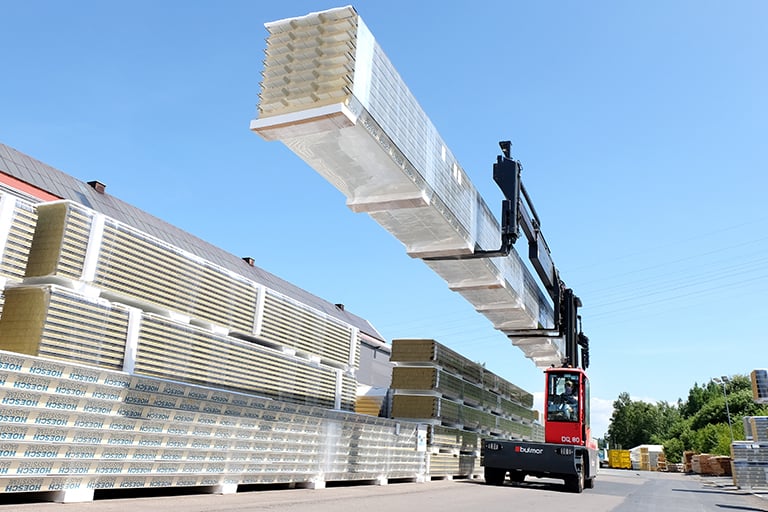

Why do the additional training at GRUMA?
The training refers to the industrial trucks that are used in the company
In-house training directly at your location
Competent trainers from the practice
High practical orientation ensures easy understanding
Further information on the additional qualification
The general forklift license (level 1) is usually completed on front forklifts. However, since front forklifts have a different driving behavior than, for example, sideloaders, reach trucks or high-bay stackers, drivers who are also to drive other industrial trucks in the company must complete additional training. As an employer, you must ensure thatdrivers of industrial trucks of special designs are trained separately for this purpose in accordance with DGUV Principle 308-001. This applies, for example, to reach trucks, sideloaders, three-side forklifts as well as telescopic forklifts and forklifts for container handling. The prerequisite for the additional qualification is the forklift license (level 1).

For which industrial trucks do you need additional training?
No additional training is required for classic front-end forklifts, apart from the general forklift license. However, it is necessary for special industrial trucks. This applies, for example, to reach trucks, sideloaders, three-side stackers as well as telescopic forklifts and forklifts for container handling.
The additional qualification is to be carried out for these vehicles in addition to the general training (level 1). Upon successful completion of the theoretical and practical examination, participants receive a corresponding certificate.
Contents of the additional qualification for forklift license (level 2)
Theoretical part:
- DGUV Principle 308-001
- Accident statistics, accident examples
- Stability
- Care and maintenance
Practical part:
- Instruction into the device
- Daily operational test
- Various driving exercises
Examination in theory and practice


Legal basis & participation requirements
In accordance with DGUV principle 308-001, drivers who use special industrial trucks in the company must take part in additional training.
In addition, the following prerequisites apply to participation in the training:
- Minimum age: 18 years
- Proof of basic training (forklift license level 1)
- Physical and mental fitness
GRUMA Inhouse Training
The training directly at your site.
Frequently asked questions about the forklift license (level 2)
The forklift license additional qualification (level 2) is required to operate special industrial trucks, such as
reach trucks, sideloaders, three-side stackers, telescopic stackers for container handling (reachstackers), forklifts for container handling and for handling special attachments.
The current prices for the additional qualification can be found in our training calendar.
- Minimum age is 18 years. Under supervision, trainees may also operate a forklift truck in the company if they are under 18.
- A car driver's license is not a prerequisite for forklift driving
- You should be mentally and physically able to
- General forklift license (level 1)
If you have taken your forklift training at GRUMA, it is no problem if you can no longer find your forklift license. Simply request a transcript of the driving license.
Overview: What training is required for which industrial truck?
Training in the in-house driving of industrial trucks | Front Forklift | Pedestrian controlled industrial trucks | Pedestrian controlled industrial trucks with stand / seat | Reach truck | Sideloader | High rack stacker / Three sided stacker | Telescopic stacker for container handling (reach stacker) | Forklift truck for container handling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
General qualification (level 1)
§7 Para. 1 DGUV Regulation 68 /
5.1 TRBS 11161 | ||||||||
Additional qualification (level 2)
3.3 DGUV Principle 308-001 2 | ||||||||
Operational qualification (level 3)
3.4 DGUV Principle 308-001 / § 12 Occupational Health and Safety Act3 | ||||||||
Qualification in handling
§ 7 Para. 2 DGUV Regulation 68 / 3.2 TRBS 11164 | ||||||||
Annual instruction
§ 4 DGUV Regulation 1 / § 12 Occupational Health and Safety Act5 | ||||||||
Annual instruction according to BGV A1 and BGR 199 (PPE, rescue from heights and depths) | ||||||||
Prerequisite for controlling industrial trucks
§ 7 Para. 1 DGUV Regulation 686
| ||||||||
Written assignment
§ 7 Para. 1 DGUV Regulation 68 / § 7 Para. 2 DGUV Regulation 68 / 3.7 TRBS 11167 |
Legend
Red: Should be performed by a specially trained person, such as GRUMA Academy training instructors.
Dark gray: Should be performed by the contractor.
Light gray: Should be carried out by the contractor or a specially trained person, such as the GRUMA Academy training managers.
Legal basis
(1) The employer may only assign the independent driving of industrial trucks with driver's seat or driver's platform to persons who
1. are at least 18 years old,
2. are suitable and trained for this activity
and
3. have proven their competence.
Implementation Statement:
Drivers of forklift trucks, for example, are trained and competent for this activity if they have been trained in accordance with the BG principle "Training and commissioning of drivers of industrial trucks with driver's seat and driver's platform" (DGUV Principle 308-001), have passed an examination in theory and practice, and can present proof of this.
The driving of industrial trucks by young people under the age of 18 for vocational training purposes under supervision is not considered to be independent driving. Under supervision means that the supervisor describes and specifies the respective work task and limits its location and duration. The supervisor must regularly ensure that the task is being carried out properly.
1 §7 Para. 1 DGUV Regulation 68
5.1 Operating an industrial truck with driver's seat or driver's platform
The employer can assume that the requirements described in sections 4.1 to 4.6 have been met if the qualification of an operator has been carried out in accordance with DGUV principle 308-001 "Qualification and commissioning of drivers of industrial trucks other than all-terrain telescopic forklifts". This is particularly the case if the qualification was carried out by a person certified on the basis of this principle.
5.1 TRBS 1116
3.3 Additional qualification (level 2) (DGUV principle 308-001)
As a rule, the general qualification (level 1) is carried out on forklift trucks. Therefore, if operators drive other industrial trucks in the company, they must take part in an additional qualification measure (level 2). This applies, for example, to reach trucks, sideloaders, three-side stackers, straddle carriers, straddle carriers (van carriers), telescopic forklifts for container handling (reach stackers) or forklifts for container handling. The additional qualification is to be divided into a practical part and a theoretical part, both parts are to be completed with an examination.
3.4 Operational qualification (level 3) (DGUV principle 308-001)
The company qualification (level 3) refers to the conditions of the respective company. It can therefore only be carried out in the company itself. A distinction must be made here between an equipment-related and a behavior-related part of the in-company qualification.
3.4.1 Device-related part
Equipment-related qualification is essentially instruction on the industrial trucks and their attachments available in the company. If the practical part of the general qualification does not take place directly in the company, it is often carried out with industrial trucks that differ from the industrial trucks in the company, e.g. in their design and mode of operation. For example, the number and arrangement of the actuators and pedals may be different. Therefore, it is essential that the operator of an industrial truck, before taking over another piece of equipment in the plant, is familiarized with its special features and becomes accustomed to its operation with care and caution.
3.4.2 Behavioral part
In the behavior-related part, the employer must instruct the operator in all matters that must be observed in his company. This includes, for example, instruction on the approved traffic routes, on storage, storage areas and stacking, regulations on the carriage of persons on industrial trucks, the use of attachments or trailers and the use of working platforms. Essentially, these are matters that the employer has already listed in the operating instructions to be prepared in accordance with § 5 of DGUV Regulation 68 "Industrial Trucks".
§ Section 12 Instruction - Act on the Implementation of Occupational Health and Safety Measures to Improve the Safety and Health of Employees at Work (Occupational Health and Safety Act - ArbSchG)
(1) The employer shall adequately and appropriately instruct employees on safety and health protection at work during their working hours. The instruction shall include instructions and explanations specifically geared to the employees' workplace or area of responsibility. Instruction must be provided upon hiring, changes in job duties, introduction of new work equipment or a new technology before the employee begins work. The instruction must be adapted to the development of hazards and, if necessary, repeated regularly.
(2) The employer may only assign the driving of pedestrian-controlled industrial trucks to persons who are suitable and have been instructed in their handling.
Implementation Statement:
Pedestrian-controlled industrial trucks with a driver's platform whose maximum design speed is more than 6 km/h are considered to be industrial trucks with a driver's platform. In this respect, § 7 Para. 1 applies.
3.2 Risk assessment (TRBS 1116)
(5) Special hazards in the use of work equipment which require an assignment in accordance with § 12 Paragraph 3 BetrSichV can result, for example, from
1) the possibility of unstable or dangerous operating states of the work equipment,
2) the presence of persons in the hazardous area of the work equipment,
3) the release of stored energy,
4) interactions with the working environment, work objects and with other work equipment,
5) the versatility and complexity of operating and control functions of the work equipment, e.g. steam boiler systems, . e.g. steam boiler systems,
6) the need to record and process information, the scope for decision-making and the need for coordination,
7) the lack of or limited effectiveness of existing protective measures during maintenance (compare TRBS 1112 Section 4.2).
Note: The characteristics listed as examples do not contain any statement about the permissibility of the activities and about the protective measures to be taken.
Work equipment for the use of which an authorization is required in accordance with Section 12 (3) of the German Ordinance on Industrial Safety and Health (BetrSichV) includes, for example,
1. Industrial trucks with driver's seat,
2. Industrial trucks with driver's platform,
3. Industrial trucks operated by pedestrians,
4. Telescopic forklifts,
5. Aerial work platforms,
6. Cranes,
7. Excavators and loaders,
8. Plant and work equipment if the protective measures taken for normal operation are completely or partially deactivated during maintenance.
3.2 TRBS 1116
§ 4 Instruction of the insured persons (DGUV Regulation 1)
(1) The employer shall instruct the insured persons on occupational safety and health, in particular on the hazards associated with their work and the measures to prevent them, in accordance with Section 12 (1) of the Occupational Safety and Health Act and, in the case of a temporary employment agency, in accordance with Section 12 (2) of the Occupational Safety and Health Act; the instruction must be repeated if necessary, but at least once a year; it must be documented.
(2) The employer shall communicate to the insured persons in an understandable manner the contents of the applicable accident prevention regulations and rules of the accident insurance institutions as well as the relevant governmental rules and regulations that are relevant to their field of work or to their activity.
§ Section 12 Instruction - Act on the Implementation of Occupational Health and Safety Measures to Improve the Safety and Health of Employees at Work (Occupational Health and Safety Act - ArbSchG)
(1) The employer shall adequately and appropriately instruct employees on safety and health protection at work during their working hours. The instruction shall include instructions and explanations specifically geared to the employees' workplace or area of responsibility. Instruction must be provided upon hiring, changes in job duties, introduction of new work equipment or a new technology before the employee begins work. The instruction must be adapted to the development of hazards and, if necessary, repeated regularly.
§ 12 Occupational Health and Safety Act
(1) The employer may only entrust the independent driving of industrial trucks with driver's seat or driver's platform to persons who
1. are at least 18 years old,
2. are suitable and trained for this activity and
3. have proven their competence.
Implementation Statement:
Drivers of forklift trucks, for example, are trained and competent for this activity if they have been trained in accordance with the BG principle "Training and commissioning of drivers of industrial trucks with driver's seat and driver's platform" (DGUV Principle 308-001), have passed an examination in theory and practice, and can present proof of this.
The driving of industrial trucks by young people under the age of 18 for vocational training purposes under supervision is not considered to be independent driving. Under supervision means that the supervisor describes and specifies the respective work task and limits its location and duration. The supervisor must regularly ensure that the task is being carried out properly.
(1) The employer may only entrust the independent driving of industrial trucks with driver's seat or driver's platform to persons who
1. are at least 18 years old,
2. are suitable and trained for this activity and
3. have proven their competence.
Implementation Statement:
Before issuing the written assignment, both a device-specific instruction and an instruction with regard to the operational conditions are required; see also BG-Grundsatz "Ausbildung und Beauftragung der Fahrer von Flurförderzeugen mit Fahrersitz und Fahrerstand" (BGG 925). The assignment can be made, for example, by means of a driver's license and is only valid for the company for which the assignment was made. The driver's license is not transferable to other companies.
The assignment should be withdrawn if the insured is unable to demonstrate sufficient and regular driving experience over a one-year period.
§7 Para. 2 Order to control industrial trucks (DGUV Regulation 68)
(2) The employer may only assign the driving of pedestrian-controlled industrial trucks to persons who are suitable and have been instructed in their handling.
DA to §7 Para. 2:
Pedestrian-controlled industrial trucks with a driver's platform, whose maximum design speed is more than 6km/h, are considered as industrial trucks with a driver's platform. In this respect, §7 Para. 1 applies.
§ 7 Para. 2 DGUV Regulation 68
3.7 Assignment of employees (TRBS 1116)
(1) The assignment of employees must be traceable. This can be done, for example, by means of a driver or operator ID card, a documented work order, a permit or by means of corresponding operational documentation such as organizational manuals. The assignment is always only valid for the work area, the activities or the work equipment for which it was issued.
For assignments relating to one-off activities, e.g. certain maintenance tasks, release or permission certificates have proven effective (cf. Section 4.4 TRBS 1112).
(2) The assignment shall be withdrawn if there are special reasons, e.g. doubts about the competence or sufficient qualification, e.g. after accidents and near-accidents,
indication of an employee that he no longer fulfills the requirements for the assignment.
(3) When commissioning in accordance with § 12 Paragraph 3 BetrSichV, the requirements of § 22 Youth Employment Protection Act, for example, must be observed.
3.7 TRBS 1116
Overview: Which training is required for which industrial truck
Forklift license at GRUMA
Even celebrities get their forklift license at GRUMA

- After Susanne Rohrer, Dr. Christine Theiss and Dieter Thoma, Sven Hannawald is now also the happy owner of a forklift license from the GRUMA Academy. Find out how he did during the training and what he needs the license for in our article.

- Dieter Thoma: former ski jumper, TV presenter and now also the happy owner of a forklift license from the GRUMA Academy. Find out how he did during the training and what he needs the license for in our article.

- Driving a forklift for a good cause: With her participation in the Promi-StaplerCup 2015, Dr. Christine Theiss is collecting donations for children's, youth and elderly aid. For this purpose, the former kickboxing world champion and presenter completed a forklift training course at GRUMA.
Downloads
Flyer additional training forklift
Training Program of the GRUMA Academy 2023
Template written assignment for driving industrial trucks | Written driving assignment
Training & assignment of drivers of industrial trucks with driver's seat and driver's platform | Overview
4 x 4 Merkregel Forklift Truck | Daily Operational Test
Operating Instructions Template | Handling Industrial Trucks
Proof of driving hours 1-day forklift training
Further offers of the GRUMA Academy

- Do you already know our online trainings? Complete your training now from the comfort of your PC. You determine the time!

- We instruct your operators of industrial trucks, cranes, aerial work platforms, earth-moving machines and co. in accordance with the statutory regulations.

- In just one day, you will learn all the relevant knowledge for the crane license in theory and practice.

- We train you for the use of telescopic forklifts both with a rigid superstructure, with a rotating upper carriage or also as an elevating work platform.